Gambling has a rich and deeply embedded history within the cultural fabric of the United States, captivating millions of individuals who engage in various forms of betting and gaming activities each year. From the glittering casinos of Las Vegas to the bustling racetracks scattered across the nation, the allure of gambling beckons individuals from all walks of life, promising excitement, entertainment, and the tantalizing prospect of financial gain. Yet, beneath the veneer of glitz and glamour lies a darker reality: for a significant subset of individuals, gambling transcends mere recreation and evolves into a debilitating addiction that exacts a profound toll not only on the gambler but also on their families, communities, and society at large.
In this article, we’ll explore the labyrinthine world of gambling addiction, navigating through the statistics and data that unravel this complex phenomenon in the United States. Our objective is to illuminate the scale and severity of problem gambling addiction within the nation, a pressing public health issue often hidden in the shadows. To achieve this, we’ll delve into the latest prevalence rates, demographic nuances, economic impacts, and recovery efforts.
-
Facts on Gambling Addiction: Editor’s Picks
- Prevalence of Gambling Addiction: Approximately 2 million US adults are severely addicted to gambling, with another 4 to 6 million having mild to moderate gambling problems. This highlights the widespread nature of the issue across the country.
- The Economic Impact: The annual economic cost of gambling addiction in the US is estimated to range from $6 billion to $7 billion, covering healthcare, job loss, and criminal justice expenses. This underscores the significant financial burden on both individuals and society.
- Healthcare and Productivity Losses: Problem gambling may cost the US healthcare system up to $1 billion annually, with lost productivity estimated to range from $6 billion to $10 billion annually due to absenteeism and unemployment.
- Demographic Trends: Young adults (ages 18 to 24) and older adults (age 65 and older) are particularly vulnerable to gambling issues.
- Gender Gap: The gap in gambling addiction is narrowing, as there is an increase in problem gambling among women.
- Economic Status: Lower socioeconomic status, certain racial and ethnic groups, and lower education levels are associated with higher rates of problem gambling.
- Internet Gambling Growth: The rise of Internet gambling has made gambling more accessible, with young adults, especially males, being the fastest-growing demographic engaging in online betting.
- Recovery and Treatment: Only about 10% of those with a severe gambling problem seek professional help. Cognitive-behavioral therapy and support groups like Gamblers Anonymous are effective treatments, though relapse rates can be high.
- Prevention and Early Intervention: Education and awareness programs can significantly reduce the incidence of gambling problems, emphasizing the importance of early support and interventions.
Prevalence Of Gambling Addiction
Gambling addiction poses a significant challenge in both the United States and the United Kingdom, impacting millions of adults. Insights from authoritative bodies such as the National Council on Problem Gambling (NCPG) and the Gambling Commission underscore the extensive reach and gravity of this issue.
- In the United States, the National Council on Problem Gambling (NCPG) estimates that around 2 million adults meet the criteria for severe gambling addiction. Meaning that their level of addiction significantly interferes with their daily lives.
Graph showing that Approximately 2 million US adults are severely addicted to gambling - According to the National Council on Problem Gambling (NCPG), approximately 2-3% of Americans exhibit symptoms of problem gambling.
- The NCPG also reports that an additional 4 to 6 million adults in the US are considered to have mild to moderate gambling problems.
The NCPG reports that an additional 4 to 6 million adults in the US are considered to have mild to moderate gambling problems - According to the American Gaming Association, the commercial casino industry alone generates over $90 billion in revenue annually.
- In the United Kingdom, the Gambling Commission’s latest report suggests that approximately 0.5% of the adult population suffers from gambling-related harm.
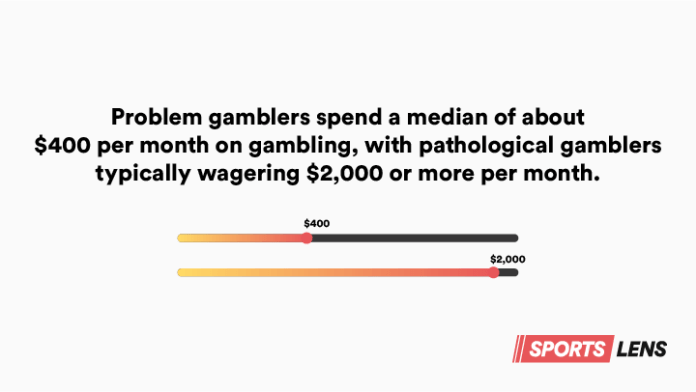
- Problem gamblers spend a median of about $400 per month on gambling, with pathological gamblers typically wagering $2,000 or more per month.
Problem gamblers spend a median of about 400 per month on gambling with pathological gamblers typically wagering 2000 or more per month - Data from the Gambling Commission indicates that approximately 340,000 adults in the UK are classified as problem gamblers, with up to 2 million at risk of developing a gambling addiction
Sources: Louisiana’s Department of Health, Minnesota Department of Human Services, NCPG, American Gaming Association, United Kindom Parliament, Gambling Commission, A Randomized Trial of Brief Interventions for Problem and Pathological Gamblers
The Economic Impact Of Gambling Addiction
The economic impact of gambling addiction is profound, particularly in the United States, where annual costs are estimated to be between $6 billion and $7 billion. These expenses encompass healthcare, job displacement, and legal fees, highlighting the seriousness of the problem. Those affected by this addiction often find themselves burdened with significant debts, resorting to illicit activities and facing unemployment, ultimately leading to financial distress and bankruptcy. Recognizing these economic ramifications is vital as they have far-reaching effects.
- In the US, it’s estimated that the annual cost to the economy ranges from $6 billion to $7 billion, covering healthcare, job loss, and criminal justice expenses.
Graph showing that in the US its estimated that the annual cost to the economy ranges from 6 billion to 7 billion - Gamblers often accumulate substantial debts, borrowing money from friends, family, or financial institutions. They may also resort to illegal activities, such as theft or embezzlement. As a result, they may experience financial ruin, bankruptcy, and loss of assets, including homes, vehicles, and savings.
- Gambling addiction can result in job loss due to absenteeism, reduced productivity, and in some cases, termination of employment. The exact cost of gambling-related job loss is challenging to quantify, but it contributes significantly to the estimated economic costs of problem gambling.
- According to the Gambling Impact and Behavior Study, 19.2% of pathologic gamblers have filed bankruptcy, whereas only 5.5% and 4.7% of low-risk and at-risk gamblers, respectively, have filed bankruptcy
- The average social cost of one individual who has a gambling disorder has been estimated at $9,393.
- The increased need for social services among problem gamblers and their families adds to the economic impact. While specific numbers can vary, the costs associated with social services, including counseling, welfare, and homelessness programs, contribute to the overall economic burden.
Sources: NCPG, Comprehensive Psychiatry, Oregon Health Authority
Demographic Trends In Gambling Addiction
Demographic patterns in gambling addiction reveal distinct trends. Young adults (ages 18-24) and older adults (age 65+) are particularly vulnerable. While historically, men had higher rates, recent trends show a narrowing gender gap. Those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds, Native and Black Americans, and individuals with lower education levels are disproportionately affected. Strong correlations exist between gambling addiction and other mental health disorders. The rise of online gambling, especially among young males, is a rapidly growing concern.
Here are some key statistics highlighting how gambling addiction affects various demographic groups:
- A report from the National Council on Problem Gambling (NCPG) suggests that young people (ages 18 to 24) are two to three times more likely to experience a gambling problem than adults.
- Older adults (age 65 and older) also represent a vulnerable group, particularly those who frequent casinos as a leisure activity, with some studies indicating that up to 10% of this age group faces gambling issues.
- Men are 2-3 times more likely to develop gambling problems than women, but the gender gap in gambling addiction is narrowing. Recent studies indicate that while men are still more likely to gamble and experience gambling-related problems, the rate of problem gambling among women is increasing, particularly among certain forms of gambling like online betting and slot machines.
- Individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds are disproportionately affected by gambling addiction. This demographic is more likely to see gambling as a way out of financial hardship, leading to higher rates of problem gambling. Ho
- Research has shown that Native Americans and Black Americans have higher rates of problem gambling compared to White Americans.
- Individuals with lower levels of education are more likely to experience problem gambling than those with higher education levels.
- There is a strong correlation between problem gambling and other mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, and substance use disorders.
- The rise of internet gambling has changed the landscape of gambling addiction, making it more accessible to a broader audience. Young adults, particularly males, are the fastest-growing demographic participating in online gambling.
Sources: National Council on Problem Gambling, The Reciprocal Association between Problem Gambling and Mental Health Symptoms
Recovery And Treatment
Recovery and treatment for gambling addiction are critical components in addressing the issue, with various approaches and success rates. Within the United States and the UK, a range of approaches and support systems are accessible to aid individuals in their efforts to overcome gambling addiction.Here are some statistics and insights into the treatment and recovery landscape for gambling addiction in the United States:
- According to the National Council on Problem Gambling, about 1% of U.S. adults have a severe gambling problem, yet only about 10% of those individuals seek help from professionals. This low treatment-seeking rate can be attributed to stigma, lack of awareness, or denial of the problem.
Only about 10 of those with a severe gambling problem seek professional help - Treatment for gambling addiction can include therapy (such as cognitive-behavioral therapy [CBT]), support groups (like Gamblers Anonymous), and sometimes medication.
- CBT has been shown to be particularly effective, with studies indicating that up to 70% of participants show improvement after treatment. However, relapse rates can be high, with some studies suggesting that more than half of individuals may return to gambling after treatment.
- Success rates for gambling addiction treatment vary widely, depending on the type of treatment, the measurement of success, and the follow-up period.
- Participation in support groups like Gamblers Anonymous is associated with higher rates of recovery. The exact success rate of Gamblers Anonymous is difficult to quantify due to the anonymous nature of the program and the lack of formal studies, but anecdotal evidence and self-reports from participants suggest that it plays a crucial role in many individuals’ recovery journeys.
- Statistics on prevention and early intervention indicate that education and awareness programs can reduce the incidence of gambling problems. Schools, communities, and healthcare providers play key roles in identifying at-risk individuals and providing early support before a full-blown addiction develops.
- In the US, programs like Gamblers Anonymous offer peer support, while professional counseling and outpatient treatment programs provide more structured therapy. The UK’s National Health Service (NHS) has begun to offer specialized services for gambling addiction, recognizing the need for targeted support.
Sources: Gambling Disorder and Stigma: Opportunities for Treatment and Prevention, A Randomized Trial of Brief Interventions for Problem and Pathological Gamblers, Helping You Helps Me: Giving and Receiving Social Support in Recovery Groups for Problem Gamblers
Conclusion
Gambling addiction poses a significant public health challenge, not only in the United States but around the globe, necessitating a concerted effort to stem its rising tide. The statistics outlined herein underscore the profound urgency for developing robust mechanisms for prevention, intervention, and ongoing support to tackle this pervasive issue effectively. As we navigate the multifaceted ramifications of gambling addiction, it becomes increasingly evident that a collaborative approach, encompassing policymakers, healthcare practitioners, educators, and the wider community, is critical to alleviating the burden on individuals and society at large.
This in-depth exploration of gambling addiction statistics sheds light on the intricate dynamics at play, reinforcing the necessity for a sustained commitment to research, education, and policy reform. Through such endeavors, we can enhance public awareness, foster a deeper understanding of gambling addiction, and implement evidence-based strategies aimed at preventing the onset, intervening early in cases of emerging issues, and providing comprehensive support for those affected.
FAQ
What is Gambling Addiction?
Pathological gambling, colloquially referred to as gambling disorder, represents the extreme end of the gambling spectrum, characterized by compulsive behavior and an inability to control one’s gambling impulses despite adverse consequences. It is a condition that knows no bounds, affecting individuals irrespective of age, gender, socioeconomic status, or cultural background. As the stakes escalate and losses mount, the insidious grip of gambling addiction tightens its hold, leaving a trail of devastation in its wake.